

Fishmeal is obtained from small fish (used whole, including the entrails) or from the carcasses of large fish (salmon, trout, sturgeon, tuna), waste of the choices for baby food and for gastronomy. The mass is then crushed to extract any fish oil, then the product is cooled, dehydrated and ground to obtain a powder. Fishmeal is an important food used in animal husbandry and in aquaculture. It is also the main ingredient of the commonly marketed feed for aquarium fish.

Human nutrition also involves the consumption of fishmeal, but only top-quality parts of the fish are used and the finished product is free of additives and preservatives that prevent rancidity of fats (allowed only in feed for dogs and cats).
This article compares the nitrogen/protein determination in fishmeal by using NDA 702 Dumas Nitrogen Analyzer and UDK 169 Automatic Kjeldahl Analyzer with AutoKjel Autosampler. The specific methods used in this study are summarized briefly here.

The Kjeldahl and Dumas techniques are primary methods for nitrogen and protein determination, working in accordance with international standards such as AOAC, AACC, ASBC, ISO, IFFO, OIV. Both Kjeldahl and Dumas techniques are officially approved for the determination of the protein content in fishmeal. Performances of VELP Kjeldahl system and Dumas unit were evaluated by participating in the Proficiency Testing Program organized by BIPEA (Bureau Interprofessionnel d'Etudes Analytiques). The obtained results (as % Protein) were compared with the BIPEA assigned values. However, they differ in many aspects, including sample preparation, analytical procedures, and obtained values.

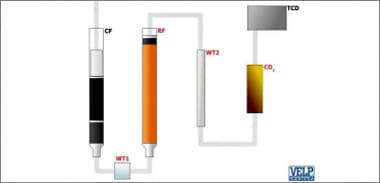
The principle of the Dumas method is to convert nitrogen present in the sample into gaseous NOx by complete combustion in a furnace maintained at 950 - 1.100 °C. The final product (NOx) is then reduced to N2 and measured using the thermal conductivity detector. The Dumas method starts with a combustion furnace (CF) to burn the sample, obtaining elemental compounds. Water is removed by a first physical trap (WT1 - DriStep™), placed after the combustion, and a second chemical one (WT2). Between the two, the elemental substances passed through a reduction furnace (RF). The auto-regenerative CO2 absorbers (CO2) let pass only the elemental nitrogen that is detected by the LoGas™ innovative Thermal Conductivity Detector (TCD) with no requirement for a reference gas. The NDA 702 is controlled via PC through the intuitive DUMASoft™.

The Kjeldahl method consists of a procedure of catalytically supported mineralization of organic material in a boiling mixture of sulfuric acid and sulfate salt at digestion temperatures higher than 400 °C. During the process, the organically bonded nitrogen is converted into ammonium sulfate. Alkalizing the digested solution liberates ammonia which is quantitatively steam distilled and determined by titration.
BIPEA Fishmeal ID: 11-0313-0217 Dumas protein: assigned value: 70.1 acceptability range: 68.0 -72.2 Kjeldahl protein: assigned value: 69.0 acceptability range: 66.9- 71.1. The sample is ground by using a laboratory grinder (particle size 1 mm).

NDA 702 Preliminary Operations. Following the operating manual to start the NDA 702, the following parameters are set: Temperature Combustion reactor (Code A00000158): 1030 °C Temperature Reduction reactor (Code A00000226): 650 °C Flow rate MFC1 He: 190 ml/min Flow rate MFC2 He: 220 ml/min. Condition the system by testing 2 EDTA standard (Code A00000149) and 3 to 5 empty tin foils (Code A00000153) as a checkup. Verify the calibration curve with one or more tests as standard by testing EDTA, used for the curve creation.
Weigh around 50 mg of sample in tin foil directly on the analytical balance. Close the tin foil, obtain a capsule, and load it into the autosampler.

The following fields are filled in the database of the software DumasoftTM: Sample name, Weight, Method, Sample type, Calibration number The “FEED FOR ANIMALS, DRY” method shows the following parameters:
Protein factor: 6.25 O2 flow rate: 400 ml/min O2 factor: 1.6 ml/mg
Press to start the analysis. Analysis time: from 3 minutes for one run.
Results have been obtained with the following calibration curve:
in a range of 0 - 7 mg N with 7 measurements of EDTA standard (%N = 9.58) (Code A00000149).
The data obtained are included in the tolerance admitted by the EDTA certificate.

1. Sample digestion Weight about 1.0 grams in a nitrogen-free weighing boat (Code CM0486000) and transfer in a test tube. In each test tube add:
• 2 catalyst tablets VCM (code A00000274; 3.5 g K2SO4, 0.1 g CuSO4 5H20 Missouri)
• 2 antifoam tablets VS (Code A00000283)
• 20 ml concentrated sulfuric acid (96-98%)
• 5 ml hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
2. Distillation and Titration
The test tubes are cooled down to 50-60 °C. The UDK 169 unit is conditioned by performing the Automatic Checkup in Menu-System and a Washdown. The samples are distilled by selecting the predefined methods n°7.

The obtained values fall within the expected protein range indicated by BIPEA, demonstrating the high performance of both VELP Analytical Instruments, Kjeldahl system and Dumas unit NDA 702. Excellent repeatability is ensured with both techniques, as demonstrated by low RSD values.

TNDA 702 Dumas combustion Elemental Analyzer with high productivity and non-stop performance, is indeed ideal for high throughput, being fully automated and requiring just 3-4 minutes per analysis. In addition, the VELP NDA Series provides the highest precision on the market with the lowest detection limit (0.001 mgN). It is ideal for those difficult samples with a very low amount of nitrogen, especially in the environmental sector. The NDA Series is completely controlled and managed by the PC, using the powerful DUMASoftTM.

VELP Kjeldahl system, using genuine catalyst tablets KjTabsTM, is still a robust solution for protein determination in the food and feed field. It has been designed to maximize automation, liberating laboratory staff, and providing the best conditions for reproducible results. In addition to the objectives for improving the Kjeldahl analysis, substantial effort has been invested in creating eco-friendly equipment-eco in terms of ecology, and also in terms of economy.

Velp DK digesters are traditional digesters, consisting of an aluminum heating block to offer high thermal homogeneity, heating up to 450 °C. The temperature of the block is constantly controlled by a microprocessor.
SPECIFICATIONS
Technique |
Sample quality (mg) |
Nitrogen % |
Protein % |
| Dumas | 50.07 | 11.41 | 71.31 |
| 50.04 | 11.36 | 70.97 | |
| 49.86 | 11.45 | 71.56 | |
| Average ± SD% | 11.41 ± 0.05 | 71.28 ± 0.29 | |
| RSD% * | 0.41 | 0.41 | |
| Technique | Sample quantity (g) | Nitrogen % | Protein % |
| Kjedahl | 1.0021 | 10.93 | 68.3 |
| 1.0007 | 10.97 | 68.56 | |
| 1.0003 | 11.09 | 69.34 | |
| Average ± SD% | 11.00 ± 0.08 | 68.73 ± 0.54 | |
| RSD% * | 0.79 | 0.79 | |
| acceptability Dumas range: 68.0 - 72.2 % P | |||
| acceptability Kjeldahl range: 66.9 - 71.1 % P | |||
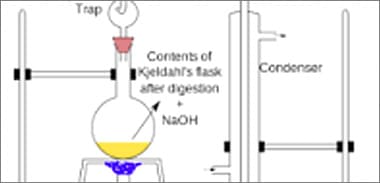
The main advantages of the Dumas method are its ease of use, speed, safety, and high level of automation that guarantees unattended operations in the laboratory. The Dumas method takes only a few minutes per measurement, making it considerably faster than Kjeldahl analysis, which usually takes more than an hour. Moreover, avoiding the use of toxic and potentially harmful chemicals or catalysts, the Dumas method ensures complete safety for lab operators.
On the other hand, the Kjeldahl method uses concentrated sulfuric acid and a catalyst for the digestion of the sample. As stringent standards started being applied in 1990s with regards to the use of harmful chemicals, many laboratories evaluated the Dumas method as alternative and numerous comparative studies were developed and published. A series of international standards were devised and also grain

▪ NDA 702 – N/Protein Elemental Analyzer
▪ DKL 20 – Digestion Unit
▪ JP Pump and SMS Scrubber for fumes neutralization
▪ UDK 159 – Distillation Unit
Geneq is an authorized Canadian distributor